As construction projects become increasingly complex and demanding, the safety and efficiency of tower cranes play a pivotal role in ensuring successful operations. Understanding how to identify and maintain essential tower crane parts is critical for preventing accidents and enhancing productivity on the job site. According to Robert Greene, a seasoned expert in the tower crane industry, “Regular maintenance and keen awareness of tower crane parts can be the difference between a smooth project and a disastrous incident.” This statement underscores the importance of not only recognizing the various parts of a tower crane but also implementing a systematic approach to their upkeep.
In this article, we will explore the key components that make up tower crane parts, detailing their functions and importance in crane operations. We will also discuss best practices for the ongoing maintenance of these crucial elements, ensuring that safety is prioritized while maximizing operational efficiency. By delving into expert insights and actionable maintenance strategies, we aim to equip construction professionals with the knowledge necessary to manage their tower cranes effectively and safely.
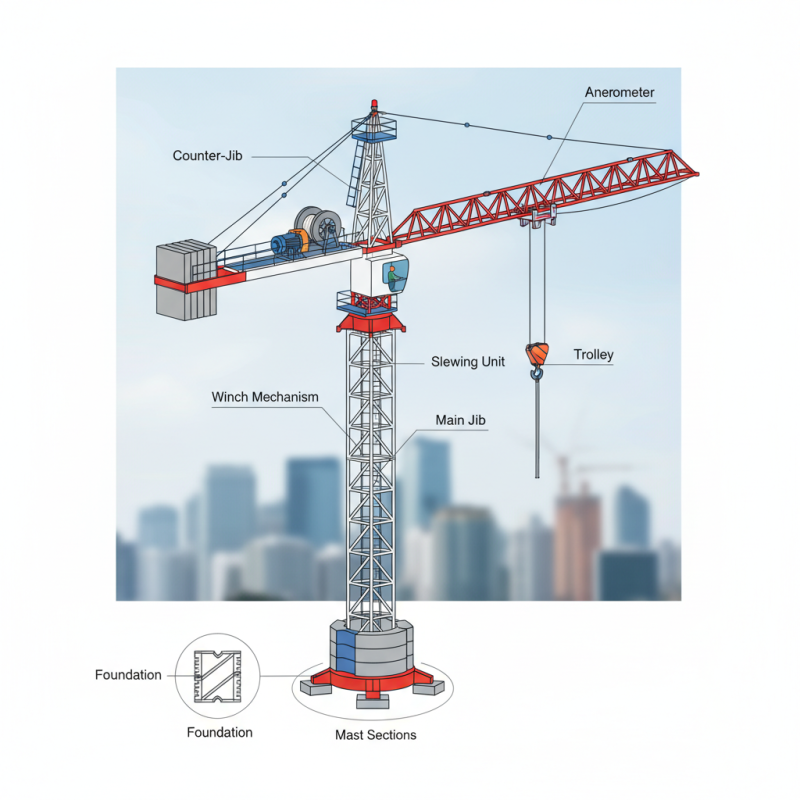
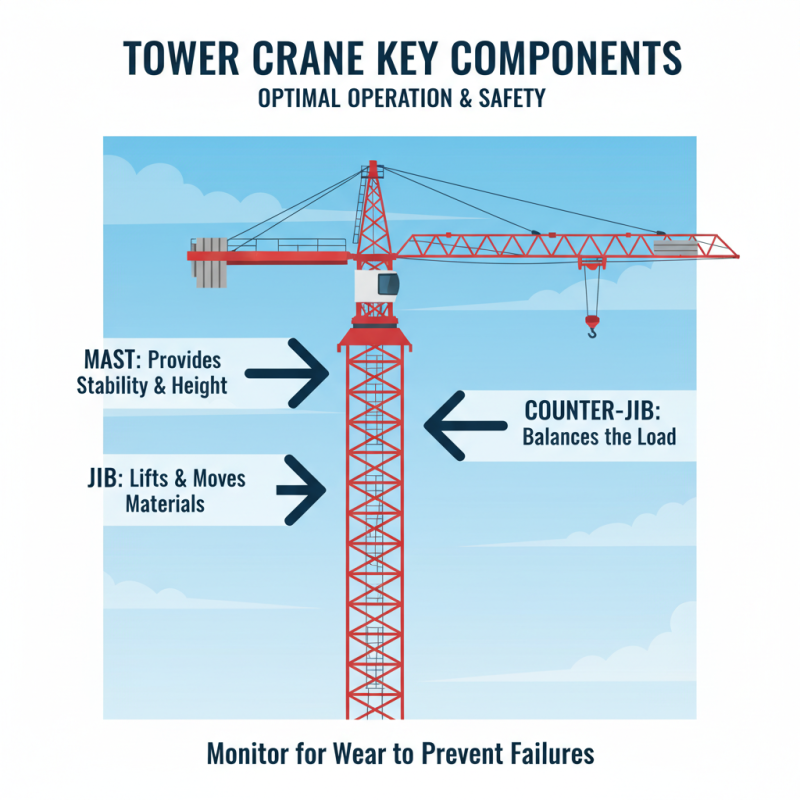
Identifying the key components of tower cranes is crucial for ensuring optimal operation and maintaining safety standards on construction sites. The main structural elements include the mast, which provides stability and height; the jib, which extends outwards to lift and move materials; and the counter-jib, which balances the load. Proper identification and understanding of these parts allow operators to monitor their condition effectively, ensuring that any wear and tear is addressed promptly to avoid operational failures.
Additionally, ancillary components like the hoist, hook, and slewing mechanism play a significant role in the crane's functionality. The hoist system must be inspected regularly to ensure it can lift loads without failure, while the slewing mechanism allows for the efficient horizontal movement of the load. Operators should also be familiar with safety features, such as limit switches and overload sensors, which are vital for preventing accidents. By recognizing and maintaining these key components, crane operators can enhance safety and improve overall efficiency, ultimately contributing to the success of the construction project.
Visual inspections are a crucial part of maintaining tower cranes, ensuring that all components function correctly and safely. Regular assessments should focus on key parts such as the boom, cab, and counterweights. When conducting a visual inspection, look for signs of wear, corrosion, or any deformation in the structure. Pay special attention to the connections and welds, as these areas are critical to the crane's overall integrity. Anomalies such as cracks or rust can indicate potential failure points that need immediate attention.
Tips for Effective Inspections:
- Always conduct inspections before and after use, making it a part of the daily routine.
- Use a checklist to ensure no part is overlooked during the assessment.
- If possible, take photographs of components to track changes over time.
Additionally, it is important to inspect the tower crane's operational features, including switches and controls, as these can affect functionality and safety. Keep an eye on the cable systems and pulleys, ensuring that there is no fraying or misalignment. Regular visual inspections help in identifying minor issues before they escalate, promoting both safety and efficiency on the job site.
Tips for Operational Checks:
- Test all controls while the crane is idle to pinpoint any irregularities.
- Observe the crane during operation from a safe distance to catch any unusual movements or sounds.
Preventive maintenance is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of tower cranes. Regular inspections and servicing of essential components such as cables, pulleys, and braking systems can help identify wear and tear before they lead to significant failures.
Establishing a routine maintenance schedule based on the hours of operation or usage frequency allows for timely checks and replacements, minimizing the risk of accidents on the job site. Additionally, keeping detailed records of maintenance activities can aid in understanding the crane's operational history and predicting potential issues.
Training operators and maintenance personnel on the significance of preventive practices is equally important. They should be informed about the specific parts that require regular attention and the signs of wear that should not be overlooked. Incorporating technology, such as monitoring systems that track performance metrics and alert maintenance teams to potential problems, can enhance safety measures and operational efficiency. By fostering a culture of safety and proactive maintenance, the longevity of the crane can be extended while ensuring that it operates within safety standards.

Tower cranes are vital for large construction projects, but they are not immune to common issues that can compromise safety and efficiency. One frequent problem involves the crane's hoist mechanism. According to industry reports, approximately 30% of crane accidents are attributed to hoisting failures, often caused by worn-out components or insufficient maintenance. Regular inspections of the hoist ropes and drum, along with adherence to manufacturer maintenance schedules, can significantly mitigate these risks.
Another commonly encountered issue is the wear and tear on tower crane joints and connections. A study by the Construction Industry Institute found that nearly 25% of structural failures in tower cranes were linked to connection failures. Keeping an eye on the condition of pins, bolts, and other fastening mechanisms is crucial. Implementing a routine check to ensure all joints are secure and free from corrosion can prevent potential catastrophic failures.
**Tips:** Always follow a rigorous inspection checklist before each shift to catch any discrepancies early. For extended crane lifespans, consider creating a dedicated maintenance log to track inspections and repairs, ensuring that no vital checks are overlooked. By staying proactive and well-informed about these common issues, operators can enhance both the safety and efficiency of tower crane operations.
Regularly testing and updating crane equipment is crucial for ensuring operational safety and efficiency. One of the best practices includes implementing a comprehensive inspection routine. This involves checking key components such as the hoist, brake systems, and wire ropes for wear and tear. Especially in high-use environments, scheduling these inspections monthly or quarterly can prevent minor issues from escalating into major failures.
Tips: Always document your inspections thoroughly, noting any concerns and the actions taken. This documentation not only provides a history of maintenance but also assists in identifying recurring problems that may need further attention. Furthermore, consider involving experienced personnel for the evaluations, as their expertise can be invaluable in spotting potential hazards.
Updating crane equipment is equally important and should not be overlooked. Manufacturers often release updates to improve performance or rectify safety concerns. Staying informed about these updates and implementing them promptly can greatly enhance the reliability of your equipment. Engage in regular training sessions for operators, focusing on new equipment features and best safety practices to maintain a culture of safety and efficiency in your operations.
Tips: Develop a schedule for training and refreshers that aligns with new updates to ensure all personnel remain knowledgeable and compliant with the latest safety protocols.
| Part Name | Function | Common Issues | Maintenance Frequency | Inspection Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hoist Mechanism | Lifts and lowers loads | Wear and tear, noise | Monthly | Visual and operational tests |
| Slew Ring | Allows rotation of the crane | Play or rough movement | Yearly | Lubrication check, testing |
| Counterweights | Provides stability | Displacement, corrosion | Bi-annual | Visual inspection |
| Wire Rope | Supports lifting loads | Fraying, kinks | Monthly | Visual and tensile strength test |
| Control System | Manages crane operations | Malfunctions, signal loss | Quarterly | Functional test and diagnostics |